| Exit Print View | |
Troubleshooting Guide for HotSpot VM |
 |
1. Diagnostic Tools and Options
2.1.1 Heap Allocation Profiles (heap=sites)
2.1.3 CPU Usage Sampling Profiles (cpu=samples)
2.1.4 CPU Usage Times Profile (cpu=times)
2.4.2 Attaching to a Core File on the Same Machine
2.4.3 Attaching to a Core File or a Hung Process from a Different Machine
2.5.1.6 Reachable Objects Query
2.5.1.7 Instance Counts for All Classes Query
2.5.3.1 What is keeping an object alive?
2.5.3.2 Where was this object allocated?
2.7.1 Heap Configuration and Usage
2.7.2 Heap Histogram of Running Process
2.7.3 Heap Histogram of Core File
2.7.4 Getting Information on the Permanent Generation
2.11.2 Printing Stack Trace From Core Dump
2.12.1 Example of -gcutil Option
2.12.2 Example of -gcnew Option
2.12.3 Example of -gcoldcapacity Option
2.16 Operating-System-Specific Tools
2.16.1 Solaris Operating System
2.16.3 Windows Operating System
2.16.4 Tools Introduced in Solaris 10 OS
2.16.4.1 Improvements in pmap Tool
2.16.4.2 Improvements in pstack Tool
2.16.4.3 Using the DTrace Tool
Probe Providers in Java HotSpot VM
2.17 Developing Diagnostic Tools
2.17.1 java.lang.management Package
2.17.2 java.lang.instrument Package
3. Troubleshooting Memory Leaks
4. Troubleshooting System Crashes
5. Troubleshooting Hanging or Looping Processes
6. Integrating Signal and Exception Handling
This chapter describes in detail the troubleshooting tools that are available in JDK 7. In addition, the chapter lists operating-system-specific tools that may be used in conjunction with these troubleshooting tools. Finally, the chapter explains how you can develop new tools using the APIs provided with JDK 7.
The chapter contains the following sections:
The Heap Profiler (HPROF) tool is a simple profiler agent shipped with the JDK release. It is a dynamically linked library that interfaces with the Java VM using the Java Virtual Machine Tools Interface (JVM TI). The tool writes profiling information either to a file or to a socket in ASCII or binary format. This information can be further processed by a profiler front-end tool.
The HPROF tool is capable of presenting CPU usage, heap allocation statistics, and monitor contention profiles. In addition, it can report complete heap dumps and states of all the monitors and threads in the Java virtual machine. In terms of diagnosing problems, HPROF is useful when analyzing performance, lock contention, memory leaks, and other issues.
In addition to the HPROF library, the JDK release includes the source for HPROF as JVM TI demonstration code. This code is located in the $JAVA_HOME/demo/jvmti/hprof directory.
The HPROF tool is invoked as follows:
$ java -agentlib:hprof ToBeProfiledClass
Depending on the type of profiling requested, HPROF instructs the virtual machine to send it the relevant events. The tool then processes the event data into profiling information. For example, the following command obtains the heap allocation profile:
$ java -agentlib:hprof=heap=sites ToBeProfiledClass
The complete list of options is printed when the HPROF agent is provided with the help option, as shown below.
$ java -agentlib:hprof=help
HPROF: Heap and CPU Profiling Agent (JVMTI Demonstration Code)
hprof usage: java -agentlib:hprof=[help]|[<option>=<value>, ...]
Option Name and Value Description Default
--------------------- ----------- -------
heap=dump|sites|all heap profiling all
cpu=samples|times|old CPU usage off
monitor=y|n monitor contention n
format=a|b text(txt) or binary output a
file=<file> write data to file java.hprof[{.txt}]
net=<host>:<port> send data over a socket off
depth=<size> stack trace depth 4
interval=<ms> sample interval in ms 10
cutoff=<value> output cutoff point 0.0001
lineno=y|n line number in traces? y
thread=y|n thread in traces? n
doe=y|n dump on exit? y
msa=y|n Solaris micro state accounting n
force=y|n force output to <file> y
verbose=y|n print messages about dumps y
Obsolete Options
----------------
gc_okay=y|n
<>
Examples
--------
- Get sample cpu information every 20 millisec, with a stack depth of 3:
java -agentlib:hprof=cpu=samples,interval=20,depth=3 classname
- Get heap usage information based on the allocation sites:
java -agentlib:hprof=heap=sites classname
Notes
-----
- The option format=b cannot be used with monitor=y.
- The option format=b cannot be used with cpu=old|times.
- Use of the -Xrunhprof interface can still be used, e.g.
java -Xrunhprof:[help]|[<option>=<value>, ...]
will behave exactly the same as:
java -agentlib:hprof=[help]|[<option>=<value>, ...]
Warnings
--------
- This is demonstration code for the JVMTI interface and use of BCI,
it is not an official product or formal part of the JDK.
- The -Xrunhprof interface will be removed in a future release.
- The option format=b is considered experimental, this format may change
in a future release.
By default, heap profiling information (sites and dump) is written out to java.hprof.txt (in ASCII) in the current working directory.
The output is normally generated when the VM exits, although this can be disabled by setting the “dump on exit” option to “n” (doe=n). In addition, a profile is generated when Ctrl-\ or Ctrl-Break (depending on platform) is pressed. On Solaris OS and Linux a profile is also generated when a QUIT signal is received (kill -QUIT pid). If Ctrl-\ or Ctrl-Break is pressed multiple times, multiple profiles are generated to the one file.
The output in most cases will contain IDs for traces, threads, and objects. Each type of ID will typically start with a different number than the other IDs. For example, traces might start with 300000.
The following output is the heap allocation profile generated by running the Java compiler (javac) on a set of input files. Only parts of the profiler output are shown here.
$ javac -J-agentlib:hprof=heap=sites Hello.java
SITES BEGIN (ordered by live bytes) Wed Oct 4 13:13:42 2006
percent live alloc'ed stack class
rank self accum bytes objs bytes objs trace name
1 44.13% 44.13% 1117360 13967 1117360 13967 301926 java.util.zip.ZipEntry
2 8.83% 52.95% 223472 13967 223472 13967 301927 com.sun.tools.javac.util.List
3 5.18% 58.13% 131088 1 131088 1 300996 byte[]
4 5.18% 63.31% 131088 1 131088 1 300995 com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name[]
A crucial piece of information in the heap profile is the amount of allocation that occurs in various parts of the program. The SITES record above shows that 44.13% of the total space was allocated for java.util.zip.ZipEntry objects.
A good way to relate allocation sites to the source code is to record the dynamic stack traces that led to the heap allocation. The following output shows another part of the profiler output. This output illustrates the stack traces referred to by the four allocation sites in output shown above.
TRACE 301926:
java.util.zip.ZipEntry.<init>(ZipEntry.java:101)
java.util.zip.ZipFile+3.nextElement(ZipFile.java:417)
com.sun.tools.javac.jvm.ClassReader.openArchive(ClassReader.java:1374)
com.sun.tools.javac.jvm.ClassReader.list(ClassReader.java:1631)
TRACE 301927:
com.sun.tools.javac.util.List.<init>(List.java:42)
com.sun.tools.javac.util.List.<init>(List.java:50)
com.sun.tools.javac.util.ListBuffer.append(ListBuffer.java:94)
com.sun.tools.javac.jvm.ClassReader.openArchive(ClassReader.java:1374)
TRACE 300996:
com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name$Table.<init>(Name.java:379)
com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name$Table.<init>(Name.java:481)
com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name$Table.make(Name.java:332)
com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name$Table.instance(Name.java:349)
TRACE 300995:
com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name$Table.<init>(Name.java:378)
com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name$Table.<init>(Name.java:481)
com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name$Table.make(Name.java:332)
com.sun.tools.javac.util.Name$Table.instance(Name.java:349)
Each frame in the stack trace contains class name, method name, source file name, and the line number. The user can set the maximum number of frames collected by the HPROF agent. The default limit is four. Stack traces reveal not only which methods performed heap allocation, but also which methods were ultimately responsible for making calls that resulted in memory allocation.
A heap dump is obtained using the heap=dump option. The
heap dump is in either ASCII or binary format, depending on the
setting of the format option. Tools such as jhat
(see ![]() 2.5 jhat Utility) use the binary format and
therefore the format=b option is required. When the binary
format is specified, the dump includes primitive type instance
fields and primitive array content.
2.5 jhat Utility) use the binary format and
therefore the format=b option is required. When the binary
format is specified, the dump includes primitive type instance
fields and primitive array content.
The following command produces a dump from executing the javac compiler.
$ javac -J-agentlib:hprof=heap=dump Hello.java
The output is a large file. It consists of the root set as determined by the garbage collector, and an entry for each Java object in the heap that can be reached from the root set. The following is a selection of records from a sample heap dump.
HEAP DUMP BEGIN (39793 objects, 2628264 bytes) Wed Oct 4 13:54:03 2006
ROOT 50000114 (kind=<thread>, id=200002, trace=300000)
ROOT 50000006 (kind=<JNI global ref>, id=8, trace=300000)
ROOT 50008c6f (kind=<Java stack>, thread=200000, frame=5)
:
CLS 50000006 (name=java.lang.annotation.Annotation, trace=300000)
loader 90000001
OBJ 50000114 (sz=96, trace=300001, class=java.lang.Thread@50000106)
name 50000116
group 50008c6c
contextClassLoader 50008c53
inheritedAccessControlContext 50008c79
blockerLock 50000115
OBJ 50008c6c (sz=48, trace=300000, class=java.lang.ThreadGroup@50000068)
name 50008c7d
threads 50008c7c
groups 50008c7b
ARR 50008c6f (sz=16, trace=300000, nelems=1,
elem type=java.lang.String[]@5000008e)
[0] 500007a5
CLS 5000008e (name=java.lang.String[], trace=300000)
super 50000012
loader 90000001
:
HEAP DUMP END
Each record is a ROOT, OBJ, CLS, or ARR to represent a root, an object instance, a class, or an array. The hexadecimal numbers are identifiers assigned by HPROF. These numbers are used to show the references from an object to another object. For example, in the above sample, the java.lang.Thread instance 50000114 has a reference to its thread group (50008c6c) and other objects.
In general, as the output is very large, it is necessary to use
a tool to visualize or process the output of a heap dump. One such
tool is jhat. See ![]() 2.5 jhat
Utility.
2.5 jhat
Utility.
The HPROF tool can collect CPU usage information by sampling threads. Below is part of the output collected from a run of the javac compiler.
$ javac -J-agentlib:hprof=cpu=samples Hello.java CPU SAMPLES BEGIN (total = 462) Wed Oct 4 13:33:07 2006 rank self accum count trace method 1 49.57% 49.57% 229 300187 java.util.zip.ZipFile.getNextEntry 2 6.93% 56.49% 32 300190 java.util.zip.ZipEntry.initFields 3 4.76% 61.26% 22 300122 java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass2 4 2.81% 64.07% 13 300188 java.util.zip.ZipFile.freeEntry 5 1.95% 66.02% 9 300129 java.util.Vector.addElement 6 1.73% 67.75% 8 300124 java.util.zip.ZipFile.getEntry 7 1.52% 69.26% 7 300125 java.lang.ClassLoader.findBootstrapClass 8 0.87% 70.13% 4 300172 com.sun.tools.javac.main.JavaCompiler.<init> 9 0.65% 70.78% 3 300030 java.util.zip.ZipFile.open 10 0.65% 71.43% 3 300175 com.sun.tools.javac.main.JavaCompiler.<init> ... CPU SAMPLES END
The HPROF agent periodically samples the stack of all running threads to record the most frequently active stack traces. The count field above indicates how many times a particular stack trace was found to be active. These stack traces correspond to the CPU usage hot spots in the application.
The HPROF tool can collect CPU usage information by injecting code into every method entry and exit, thereby keeping track of exact method call counts and the time spent in each method. This process uses Byte Code Injection (BCI) and runs considerably slower than the cpu=samples option. Below is part of the output collected from a run of the javac compiler.
$ javac -J-agentlib:hprof=cpu=times Hello.java CPU TIME (ms) BEGIN (total = 2082665289) Wed oct 4 13:43:42 2006 rank self accum count trace method 1 3.70% 3.70% 1 311243 com.sun.tools.javac.Main.compile 2 3.64% 7.34% 1 311242 com.sun.tools.javac.main.Main.compile 3 3.64% 10.97% 1 311241 com.sun.tools.javac.main.Main.compile 4 3.11% 14.08% 1 311173 com.sun.tools.javac.main.JavaCompiler.compile 5 2.54% 16.62% 8 306183 com.sun.tools.javac.jvm.ClassReader.listAll 6 2.53% 19.15% 36 306182 com.sun.tools.javac.jvm.ClassReader.list 7 2.03% 21.18% 1 307195 com.sun.tools.javac.comp.Enter.main 8 2.03% 23.21% 1 307194 com.sun.tools.javac.comp.Enter.complete 9 1.68% 24.90% 1 306392 com.sun.tools.javac.comp.Enter.classEnter 10 1.68% 26.58% 1 306388 com.sun.tools.javac.comp.Enter.classEnter ... CPU TIME (ms) END
In this output the count represents the true count of the number of times this method was entered, and the percentages represent a measure of thread CPU time spent in those methods.
Java VisualVM is one of the tools included in the JDK download (starting with JDK release 7 update 7). This tool is useful to Java application developers to troubleshoot applications and to monitor and improve the applications' performance. With Java VisualVM you can generate and analyze heap dumps, track down memory leaks, perform and monitor garbage collection, and perform lightweight memory and CPU profiling. The tool is also useful for tuning, heap sizing, offline analysis, and post-mortem diagnosis.
In addition, you can use existing plug-ins that expand the functionality of Java VisualVM. For example, most of the functionality of the JConsole tool is available via the MBeans tab and the JConsole plug-in wrapper tab. You can choose from a catalog of standard Java VisualVM plug-ins by choosing Plugins from the Tools menu in the main Java VisualVM window.
For comprehensive documentation for Java VisualVM, see http://download.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/visualvm/index.html
Java VisualVM allows you to perform the following troubleshooting activities:
View a list of local and remote Java applications.
View application configuration and runtime environment. For each application, the tool shows basic runtime information: PID, host, main class, arguments passed to the process, JVM version, JDK home, JVM flags, JVM arguments, system properties.
Enable and disable the creation of a heap dump when a specified application encounters an OutOfMemoryError exception.
Monitor application memory consumption, running threads, and loaded classes.
Trigger a garbage collection immediately.
Create a heap dump immediately. You can then view the heap dump in several views: summary, by class, by instance. You can also save the heap dump to your local file system.
Profile application performance or analyze memory allocation (for local applications only). You can also save the profiling data.
Create a thread dump (stack trace of the application's active threads) immediately. You can then view the thread dump.
Analyze core dumps (with Solaris OS and Linux).
Analyze applications offline, by taking application snapshots.
Get additional plug-ins contributed by the community.
Write and share your own plug-ins.
Display and interact with MBeans (after installing the MBeans tab plug-in).
When you start Java VisualVM, the main Application window opens, displaying a list of Java applications running on the local machine, a list of Java applications running on any connected remote machines, a list of any VM core dumps that were taken and saved (with Solaris OS and Linux), and a list of any application snapshots that were taken and saved.
Java VisualVM will automatically detect and connect to JMX
agents for Java applications that are running on JDK 7 or that
have been started with the correct system
properties on version 5.0. In order for the tool to detect and
connect to the agents on a remote machine, the jstatd
daemon must be running on the remote machine (see ![]() 2.13
jstatd Daemon). In cases where Java VisualVM cannot
automatically discover and connect to JMX agents that are running
in a target application, the tool provides a means for you to
explicitly create these connections.
2.13
jstatd Daemon). In cases where Java VisualVM cannot
automatically discover and connect to JMX agents that are running
in a target application, the tool provides a means for you to
explicitly create these connections.
Another useful tool included in the JDK download is the JConsole monitoring tool. This tool is compliant with Java Management Extensions (JMX). The tool uses the built-in JMX instrumentation in the Java Virtual Machine to provide information on the performance and resource consumption of running applications. Although the tool is included in the JDK download, it can also be used to monitor and manage applications deployed with the Java runtime environment.
The JConsole tool can attach to any Java application in order to display useful information such as thread usage, memory consumption, and details about class loading, runtime compilation, and the operating system.
This output helps with high-level diagnosis on problems such as memory leaks, excessive class loading, and running threads. It can also be useful for tuning and heap sizing.
In addition to monitoring, JConsole can be used to dynamically change several parameters in the running system. For example, the setting of the -verbose:gc option can be changed so that garbage collection trace output can be dynamically enabled or disabled for a running application.
The following list provides an idea of the data that can be monitored using the JConsole tool. Each heading corresponds to a tab pane in the tool.
Overview
This pane displays graphs showing, over time, heap memory usage, number of threads, number of classes, and CPU usage. This overview allows you to visualize the activity of several resources at once.
Memory
For a selected memory area (heap, non-heap, various memory pools):
Graph of memory usage over time
Current memory size
Amount of committed memory
Maximum memory size
Garbage collector information, including the number of collections performed, and the total time spent performing garbage collection.
Graph showing percentage of heap and non-heap memory currently used.
In addition, on this pane you can request garbage collection to be performed.
Threads
Graph of thread usage over time.
Live threads - Current number of live threads.
Peak - Highest number of live threads since the Java VM started.
For a selected thread, the name, state, and stack trace, as well as, for a blocked thread, the synchronizer that the thread is waiting to acquire and the thread owning the lock.
Deadlock Detection button - Sends a request to the target application to perform deadlock detection and displays each deadlock cycle in a separate tab.
Classes
Graph of number of loaded classes over time.
Number of classes currently loaded into memory.
Total number of classes loaded into memory since the Java VM started, including those subsequently unloaded.
Total number of classes unloaded from memory since the Java VM started.
VM Summary
General information, such as the JConsole connection data, uptime for the Java VM, CPU time consumed by the Java VM, complier name and total compile time, and so forth.
Thread and class summary information.
Memory and garbage collection information, including number of objects pending finalization, and so forth.
Information about the operating system, including physical characteristics, the amount of virtual memory for the running process, swap space, and so forth.
Information about the virtual machine itself, such as arguments, class path, and so forth.
MBeans
This pane displays a tree structure showing all platform and application MBeans that are registered in the connected JMX agent. When you select an MBean in the tree, its attributes, operations, notifications, and other information are displayed.
You can invoke operations, if any. For example, the operation dumpHeap for the HotSpotDiagnostic MBean, which is in the com.sun.management domain, performs a heap dump. The input parameter for this operation is the pathname of the heap dump file on the machine where the target VM is running.
As another example of invoking an operation, you can set the value of writable attributes. For example, you can set, unset, or change the value of certain VM flags by invoking the setVMOption operation of the HotSpotDiagnostic MBean. The flags are indicated by the list of values of the DiagnosticOptions attribute.
You can subscribe to notifications, if any, by using the Subscribe and Unsubscribe buttons.
JConsole can monitor both local applications and remote applications. If you start the tool with an argument specifying a JMX agent to connect to, the tool will automatically start monitoring the specified application.
To monitor a local application, execute the command jconsole pid, where pid is the process ID of the application.
To monitor a remote application, execute the command jconsole hostname:portnumber, where hostname is the name of the host running the application, and portnumber is the port number you specified when you enabled the JMX agent.
If you execute the jconsole command without arguments, the tool will start by displaying the New Connection window, where you specify the local or remote process to be monitored. You can connect to a different host at any time by using the Connection menu.
With the JDK 1.5 release, you must start the application to be monitored with the -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote option. With the JDK 7 release, no option is necessary when starting the application to be monitored.
As an example of the output of the monitoring tool, the following screen shows a chart of heap memory usage.
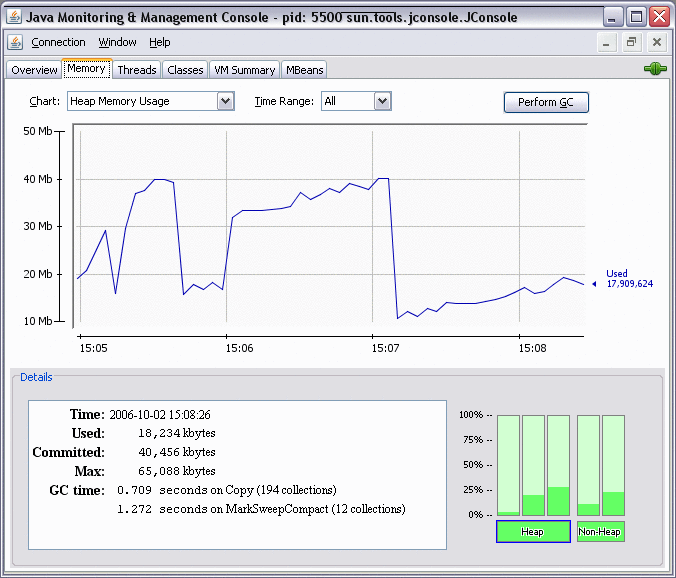
A complete tutorial on the JConsole tool is beyond the scope of this document. However, the following documents describe in more detail the monitoring and management capabilities, and how to use JConsole:
Monitoring and Management for the Java Platform
http://download.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/management/index.html
Monitoring and Management Using JMX
http://download.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/management/agent.html
Using JConsole
http://download.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/management/jconsole.html
Manual page for jconsole
http://download.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/tools/share/jconsole.html
The jdb utility is included in the JDK release as the example command-line debugger. The jdb utility uses the Java Debug Interface (JDI) to launch or connect to the target VM. The source code for jdb is included in $JAVA_HOME/demo/jpda/examples.jar.
The Java Debug Interface (JDI) is a high-level Java API that
provides information useful for debuggers and similar systems that
need access to the running state of a (usually remote) virtual
machine. JDI is a component of the Java Platform Debugger
Architecture (JPDA). See ![]() 2.17.5 Java Platform
Debugger Architecture.
2.17.5 Java Platform
Debugger Architecture.
In JDI a connector is the means by which the debugger connects to the target virtual machine. The JDK release has traditionally shipped with connectors that launch and establish a debugging session with a target VM, as well as connectors that are used for remote debugging (using TCP/IP or shared memory transports).
This JDK release also ships with several Serviceability Agent (SA) connectors that allow a Java language debugger to attach to a crash dump or hung process. This can be useful in determining what the application was doing at the time of the crash or hang.
These connectors are SACoreAttachingConnector, SADebugServerAttachingConnector, and SAPIDAttachingConnector.
These connectors are generally used with enterprise debuggers, such as as NetBeans IDE or commerical IDEs. The following subsections demonstrate how these connectors can be used with the jdb command-line debugger.
For detailed information about the connectors, see http://download.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/jpda/conninv.html#Connectors.
The command jdb -listconnectors prints a list of the available connectors. The command jdb -help prints the command usage.
For more information on the jdb utility, refer to the manual pages:
Solaris OS and Linux: jdb man page
http://download.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/tools/solaris/jdb.html
Windows: jdb man page
http://download.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/tools/windows/jdb.html
This example uses the SA PID Attaching Connector to attach to a process. The target process is not started with any special options, that is, the -agentlib:jdwp option is not required. When this connector attaches to a process it does so in read-only mode: the debugger can examine threads and the running application but it cannot change anything. The process is frozen while the debugger is attached.
The command in the following example instructs jdb to use a connector named sun.jvm.hotspot.jdi.SAPIDAttachingConnector. This is a connector name rather than a class name. The connector takes one argument called pid, whose value is the process ID of the target process (9302 in this example).
$ jdb -connect sun.jvm.hotspot.jdi.SAPIDAttachingConnector:pid=9302 Initializing jdb ... > threads Group system: (java.lang.ref.Reference$ReferenceHandler)0xa Reference Handler unknown (java.lang.ref.Finalizer$FinalizerThread)0x9 Finalizer unknown (java.lang.Thread)0x8 Signal Dispatcher running (java.lang.Thread)0x7 Java2D Disposer unknown (java.lang.Thread)0x2 TimerQueue unknown Group main: (java.lang.Thread)0x6 AWT-XAWT running (java.lang.Thread)0x5 AWT-Shutdown unknown (java.awt.EventDispatchThread)0x4 AWT-EventQueue-0 unknown (java.lang.Thread)0x3 DestroyJavaVM running (sun.awt.image.ImageFetcher)0x1 Image Animator 0 sleeping (java.lang.Thread)0x0 Intro running > thread 0x7 Java2D Disposer[1] where [1] java.lang.Object.wait (native method) [2] java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove (ReferenceQueue.java:116) [3] java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove (ReferenceQueue.java:132) [4] sun.java2d.Disposer.run (Disposer.java:125) [5] java.lang.Thread.run (Thread.java:619) Java2D Disposer[1] up 1 Java2D Disposer[2] where [2] java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove (ReferenceQueue.java:116) [3] java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove (ReferenceQueue.java:132) [4] sun.java2d.Disposer.run (Disposer.java:125) [5] java.lang.Thread.run (Thread.java:619)
In this example the threads command is used to get a list of all threads. Then a specific thread is selected with the thread 0x7 command, and the where command is used to get a thread dump. Next the up 1 command is used to move up one frame in the stack, and the where command is used again to get a thread dump.
The SA Core Attaching Connector is used to attach the debugger
to a core file. The core file may have been created after a crash
(see ![]() Chapter 4, Troubleshooting System Crashes).
The core file can also be obtained by using the gcore
command on Solaris OS or the gcore command in gdb
on Linux. Because the core file is a snapshot of the process at the
time the core file was created, the connector attaches in read-only
mode: the debugger can examine threads and the running application
at the time of the crash.
Chapter 4, Troubleshooting System Crashes).
The core file can also be obtained by using the gcore
command on Solaris OS or the gcore command in gdb
on Linux. Because the core file is a snapshot of the process at the
time the core file was created, the connector attaches in read-only
mode: the debugger can examine threads and the running application
at the time of the crash.
The following command is an example of using this connector:
$ jdb -connect sun.jvm.hotspot.jdi.SACoreAttachingConnector:\ javaExecutable=$JAVA_HOME/bin/java,core=core.20441
This command instructs jdb to use a connector named sun.jvm.hotspot.jdi.SACoreAttachingConnector. The connector takes two arguments called javaExecutable and core. The javaExecutable argument indicates the name of the Java binary. The core argument is the core file name (the core from the process with PID 20441 in this example).
In order to debug a core file that has been transported from another machine, the OS versions and libraries must match. In this case you can first run a proxy server called the SA Debug Server. Then, on the machine where the debugger is installed, you can use the SA Debug Server Attaching Connector to connect to the debug server.
In the example below, there are two machines, machine 1 and machine 2. A core file is available on machine 1 and the debugger is available on machine 2. The SA Debug Server is started on machine 1 as follows.
$ jsadebugd $JAVA_HOME/bin/java core.20441
The jsadebugd command takes two arguments. The first argument is the name of the executable. In most cases this is java, but it can be another name (in the case of embedded VMs, for example). The second argument is the name of the core file. In this example the core file was obtained for a process with PID 20441 using the gcore utility.
On machine 2, the debugger connects to the remote SA Debug Server using the SA Debug Server Attaching Connector, as with the following command:
$ jdb -connect sun.jvm.hotspot.jdi.SADebugServerAttachingConnector:\ debugServerName=machine1
This command instructs jdb to use a connector named sun.jvm.hotspot.jdi.SADebugServerAttachingConnector. The connector has one argument debugServerName, which is the hostname or IP address of the machine where the SA Debug Server is running.
Note that the SA Debug Server can also be used to remotely debug a hung process. In that case it takes a single argument which is the process ID of the process. In addition, if it is required to run multiple debug servers on the same machine, each one must be provided with a unique ID. With the SA Debug Server Attaching Connector, this ID is provided as an additional connector argument. These details are described in the JPDA documentation.
The jhat tool provides a convenient means to browse the object topology in a heap snapshot. This tool was introduced in the JDK 6 release to replace the Heap Analysis Tool (HAT).
For more information about the jhat utility, see the man page for jhat- Java Heap Analysis Tool.
The tool parses a heap dump in binary format, for example, a heap dump produced by jmap -dump.
This utility can help debug unintentional object retention. This term is used to describe an object that is no longer needed but is kept alive due to references through some path from the rootset. This can happen, for example, if an unintentional static reference to an object remains after the object is no longer needed, if an Observer or Listener fails to de-register itself from its subject when it is no longer needed, or if a Thread that refers to an object does not terminate when it should. Unintentional object retention is the Java language equivalent of a memory leak.
The tool provides a number of standard queries. For example, the Roots query displays all reference paths from the rootset to a specified object and is particularly useful for finding unnecessary object retention.
In addition to the standard queries, you can develop your own custom queries with the Object Query Language (OQL) interface.
When you issue the jhat command, the utility starts an HTTP server on a specified TCP port. You can then use any browser to connect to the server and execute queries on the specified heap dump.
The following example shows how to execute jhat to analyze a heap dump file named snapshot.hprof:
$ jhat snapshot.hprof Started HTTP server on port 7000 Reading from java_pid2278.hprof... Dump file created Fri May 19 17:18:38 BST 2006 Snapshot read, resolving... Resolving 6162194 objects... Chasing references, expect 12324 dots................................ Eliminating duplicate references..................................... Snapshot resolved. Server is ready.
At this point jhat has started a HTTP server on port 7000. Point your browser to http://localhost:7000 to connect to the jhat server.
When you are connected to the server, you can execute the
standard queries (see the following subsection) or create an OQL
query (see ![]() 2.5.2 Custom
Queries). The All Classes query is displayed by default.
2.5.2 Custom
Queries). The All Classes query is displayed by default.
The standard queries are described in these subsections.
The default page is the All Classes query, which displays all of the classes present in the heap, excluding platform classes. This list is sorted by fully-qualified class name, and broken out by package. Click on the name of a class to go to the Class query.
The second variant of this query includes the platform classes. Platform classes include classes whose fully-qualified names start with prefixes such as java, sun., javax.swing., or char[. The list of prefixes is in a system resource file called resources/platform_names.txt. You can override this list by replacing it in the JAR file, or by arranging for your replacement to occur first on the classpath when jhat is invoked.
The Class query displays information about a class. This includes its superclass, any subclasses, instance data members, and static data members. From this page you can navigate to any of the classes that are referenced, or you can navigate to an Instances query.
The Object query provides information about an object that was on the heap. From here, you can navigate to the class of the object and to the value of any object members of the object. You can also navigate to objects that refer to the current object. Perhaps the most valuable query is at the end: the Roots query (“Reference Chains from Rootset”).
Note that the object query also provides a stack backtrace of the point of allocation of the object.
The instances query displays all instances of a given class. The allInstances variant includes instances of subclasses of the given class as well. From here, you can navigate back to the source class, or you can navigate to an Object query on one of the instances.
The Roots query displays reference chains from the rootset to a given object. It provides one chain for each member of the rootset from which the given object is reachable. When calculating these chains, the tool does a depth-first search, so that it will provide reference chains of minimal length.
There are two kinds of Roots query: one that excludes weak references (Roots), and one that includes them (All Roots). A weak reference is a reference object that does not prevent its referent from being made finalizable, finalized, and then reclaimed. If an object is only referred to by a weak reference, it usually isn't considered to be retained, because the garbage collector can collect it as soon as it needs the space.
This is probably the most valuable query in jhat for debugging unintentional object retention. Once you find an object that is being retained, this query tells you why it is being retained.
This query is accessible from the Object query and shows the transitive closure of all objects reachable from a given object. This list is sorted in decreasing size, and alphabetically within each size. At the end, the total size of all of the reachable objects is given. This can be useful for determining the total runtime footprint of an object in memory, at least in systems with simple object topologies.
This query is most valuable when used in conjunction with the -exclude command line option. This is useful, for example, if the object being analyzed is an Observable. By default, all of its Observers would be reachable, which would count against the total size. The -exclude option allows you to exclude the data members java.util.Observable.obs and java.util.Observable.arr.
This query shows the count of instances for every class in the system, excluding platform classes. It is sorted in descending order, by instance count. A good way to spot a problem with unintentional object retention is to run a program for a long time with a variety of input, then request a heap dump. Looking at the instance counts for all classes, you may recognize a number of classes because there are more instances than you expect. Then you can analyze them to determine why they are being retained (possibly using the Roots query). A variant of this query includes platform classes.
The section on the All Classes query defines platform classes.
This query shows all members of the rootset, including weak references.
The New Instances query is available only if you invoke the jhat server with two heap dumps. This query is similar to the Instances query, except that it shows only new instances. An instance is considered new if it is in the second heap dump and there is no object of the same type with the same ID in the baseline heap dump. An object's ID is a 32–bit or 64–bit integer that uniquely identifies the object.
The built-in histogram and finalizer histogram queries also provide useful information.
You can develop your own custom queries with the built-in Object Query Language (OQL) interface. Click on the Execute OQL Query button on the first page to display the OQL query page, where you can create and execute your custom queries. The OQL Help facility describes the built-in functions, with examples.
The syntax of the select statement is as follows:
select JavaScript-expression-to-select [ from [instanceof] classname identifier [ where JavaScript-boolean-expression-to-filter ] ]
The following is an example of a select statement:
select s from java.lang.String s where s.count >= 100
To get useful information from jhat often requires some knowledge of the application and in addition some knowledge about the libraries and APIs that it uses. However in general the tool can be used to answer two important questions:
What is keeping an object alive?
Where was this object allocated?
When viewing an object instance, you can check the objects listed in the section entitled “References to this object” to see which objects directly reference this object. More importantly you use a Roots query to determine the reference chains from the root set to the given object. These reference chains show a path from a root object to this object. With these chains you can quickly see how an object is reachable from the root set.
As noted earlier, there are two kinds of Roots queries: one that excludes weak references (Roots), and one that includes them (All Roots). A weak reference is a reference object that does not prevent its referent from being made finalizable, finalized, and then reclaimed. If an object is only referred to by a weak reference, it usually is not considered to be retained, because the garbage collector can collect it as soon as it needs the space.
The jhat tool sorts the rootset reference chains by the type of the root, in the following order:
Static data members of Java classes.
Java local variables. For these roots, the thread responsible for them is shown. Because a Thread is a Java object, this link is clickable. This allows you, for example, to easily navigate to the name of the thread.
Native static values.
Native local variables. Again, such roots are identified with their thread.
When an object instance is being displayed, the section entitled “Objects allocated from” shows the allocation site in the form of a stack trace. In this way, you can see where the object was created.
Note that this allocation site information is available only if the heap dump was created with HPROF using the heap=all option. This HPROF option includes both the heap=dump option and the heap=sites option.
If the leak cannot be identified using a single object dump, then another approach is to collect a series of dumps and to focus on the objects created in the interval between each dump. The jhat tool provides this capability using the -baseline option.
The -baseline option allows two dumps to be compared if they were produced by HPROF and from the same VM instance. If the same object appears in both dumps it will be excluded from the list of new objects reported. One dump is specified as a baseline and the analysis can focus on the objects that are created in the second dump since the baseline was obtained.
The following example show how to specify the baseline:
$ jhat -baseline snapshot.hprof#1 snapshot.hprof#2
In the above example, the two dumps are in the file snapshot.hprof, and they are distinguished by appending #1 and #2 to the file name.
When jhat is started with two heap dumps, the Instance Counts for All Classes query includes an additional column that is the count of the number of new objects for that type. An instance is considered new if it is in the second heap dump and there is no object of the same type with the same ID in the baseline. If you click on a new count, then jhat lists the new objects of that type. Then for each instance you can view where it was allocated, which objects these new objects reference, and which other objects reference the new object.
In general, the -baseline option can be very useful if the objects that need to be identified are created in the interval between the successive dumps.
The jinfo command-line utility gets configuration information from a running Java process or crash dump and prints the system properties or the command-line flags that were used to start the virtual machine.
The utility can also use the jsadebugd daemon to query a process or core file on a remote machine. Note that the output takes longer to print in this case.
With the -flag option, the utility can dynamically set,
unset, or change the value of certain Java VM flags for the
specified Java process. See ![]() B.1.1 Dynamic
Changing of Flag Values.
B.1.1 Dynamic
Changing of Flag Values.
For more information on the jinfo utility, refer to the man page.
The following is an example of the output from a Java process.
$ jinfo 29620 Attaching to process ID 29620, please wait... Debugger attached successfully. Client compiler detected. JVM version is 1.6.0-rc-b100 Java System Properties: java.runtime.name = Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment sun.boot.library.path = /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/sparc java.vm.version = 1.6.0-rc-b100 java.vm.vendor = Sun Microsystems Inc. java.vendor.url = http://java.sun.com/ path.separator = : java.vm.name = Java HotSpot(TM) Client VM file.encoding.pkg = sun.io sun.java.launcher = SUN_STANDARD sun.os.patch.level = unknown java.vm.specification.name = Java Virtual Machine Specification user.dir = /home/js159705 java.runtime.version = 1.6.0-rc-b100 java.awt.graphicsenv = sun.awt.X11GraphicsEnvironment java.endorsed.dirs = /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/endorsed os.arch = sparc java.io.tmpdir = /var/tmp/ line.separator = java.vm.specification.vendor = Sun Microsystems Inc. os.name = SunOS sun.jnu.encoding = ISO646-US java.library.path = /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/sparc/client:/usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/sparc: /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/../lib/sparc:/net/gtee.sfbay/usr/sge/sge6/lib/sol-sparc64: /usr/jdk/packages/lib/sparc:/lib:/usr/lib java.specification.name = Java Platform API Specification java.class.version = 50.0 sun.management.compiler = HotSpot Client Compiler os.version = 5.10 user.home = /home/js159705 user.timezone = US/Pacific java.awt.printerjob = sun.print.PSPrinterJob file.encoding = ISO646-US java.specification.version = 1.6 java.class.path = /usr/jdk/jdk1.6.0/demo/jfc/Java2D/Java2Demo.jar user.name = js159705 java.vm.specification.version = 1.0 java.home = /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre sun.arch.data.model = 32 user.language = en java.specification.vendor = Sun Microsystems Inc. java.vm.info = mixed mode, sharing java.version = 1.6.0-rc java.ext.dirs = /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/ext:/usr/jdk/packages/lib/ext sun.boot.class.path = /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/resources.jar: /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/rt.jar:/usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/sunrsasign.jar: /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/jsse.jar: /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/jce.jar:/usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/lib/charsets.jar: /usr/jdk/instances/jdk1.6.0/jre/classes java.vendor = Sun Microsystems Inc. file.separator = / java.vendor.url.bug = http://java.sun.com/cgi-bin/bugreport.cgi sun.io.unicode.encoding = UnicodeBig sun.cpu.endian = big sun.cpu.isalist = VM Flags:
If you start the target Java VM with the -classpath and -Xbootclasspath arguments, the output from jinfo provides the settings for java.class.path and sun.boot.class.path. This information might be needed when investigating class loader issues.
In addition to obtaining information from a process, the jinfo tool can use a core file as input. On Solaris OS, for example, the gcore utility can be used to get a core file of the process in the above example. The core file will be named core.29620 and will be generated in the working directory of the process. The path to the Java executable and the core file must be specified as arguments to the jinfo utility, as in the following example:
$ jinfo $JAVA_HOME/bin/java core.29620
Sometimes the binary name will not be java. This occurs when the VM is created using the JNI invocation API. The jinfo tool requires the binary from which the core file was generated.
The jmap command-line utility prints memory related statistics for a running VM or core file.
The utility can also use the jsadebugd daemon to query a process or core file on a remote machine. Note that the output takes longer to print in this case.
If jmap is used with a process or core file without any command-line options, then it prints the list of shared objects loaded (the output is similar to the pmap utility on Solaris OS). For more specific information, you can use the options -heap, -histo, or -permstat. These options are described in the subsections that follow.
In addition, the JDK 7 release introduced the -dump:format=b,file=filename option, which causes jmap to dump the Java heap in binary HPROF format to a specified file. This file can then be analyzed with the jhat tool.
If the jmap pid command does not respond because of a hung process, the -F option can be used (on Solaris OS and Linux only) to force the use of the Serviceability Agent.
For more information on the jmap utility, refer to the manual page.
The -heap option is used to obtain the following Java heap information:
Information specific to the garbage collection (GC) algorithm , including the name of the GC algorithm (Parallel GC for example) and algorithm specific details (such as number of threads for parallel GC).
Heap configuration. The heap configuration might have been specified as command line options or selected by the VM based on the machine configuration.
Heap usage summary. For each generation (area of the heap), the tool prints the total heap capacity, in-use memory, and available free memory. If a generation is organized as a collection of spaces (the new generation for example), then a space-wise memory size summary is included.
The following example shows output from the jmap -heap command.
$ jmap -heap 29620 Attaching to process ID 29620, please wait... Debugger attached successfully. Client compiler detected. JVM version is 1.6.0-rc-b100 using thread-local object allocation. Mark Sweep Compact GC Heap Configuration: MinHeapFreeRatio = 40 MaxHeapFreeRatio = 70 MaxHeapSize = 67108864 (64.0MB) NewSize = 2228224 (2.125MB) MaxNewSize = 4294901760 (4095.9375MB) OldSize = 4194304 (4.0MB) NewRatio = 8 SurvivorRatio = 8 PermSize = 12582912 (12.0MB) MaxPermSize = 67108864 (64.0MB) Heap Usage: New Generation (Eden + 1 Survivor Space): capacity = 2031616 (1.9375MB) used = 70984 (0.06769561767578125MB) free = 1960632 (1.8698043823242188MB) 3.4939673639112905% used Eden Space: capacity = 1835008 (1.75MB) used = 36152 (0.03447723388671875MB) free = 1798856 (1.7155227661132812MB) 1.9701276506696428% used From Space: capacity = 196608 (0.1875MB) used = 34832 (0.0332183837890625MB) free = 161776 (0.1542816162109375MB) 17.716471354166668% used To Space: capacity = 196608 (0.1875MB) used = 0 (0.0MB) free = 196608 (0.1875MB) 0.0% used tenured generation: capacity = 15966208 (15.2265625MB) used = 9577760 (9.134063720703125MB) free = 6388448 (6.092498779296875MB) 59.98769400974859% used Perm Generation: capacity = 12582912 (12.0MB) used = 1469408 (1.401336669921875MB) free = 11113504 (10.598663330078125MB) 11.677805582682291% used
The -histo option can be used to obtain a class-wise histogram of the heap.
When the command is executed on a running process, the tool prints the number of objects, memory size in bytes, and fully qualified class name for each class. Internal classes in the HotSpot VM are enclosed in angle brackets. The histogram is useful in understanding how the heap is used. To get the size of an object you must divide the total size by the count of that object type.
The following example shows output from the jmap -histo command when it is executed on a process.
$ jmap -histo 29620 num #instances #bytes class name -------------------------------------- 1: 1414 6013016 [I 2: 793 482888 [B 3: 2502 334928 <constMethodKlass> 4: 280 274976 <instanceKlassKlass> 5: 324 227152 [D 6: 2502 200896 <methodKlass> 7: 2094 187496 [C 8: 280 172248 <constantPoolKlass> 9: 3767 139000 [Ljava.lang.Object; 10: 260 122416 <constantPoolCacheKlass> 11: 3304 112864 <symbolKlass> 12: 160 72960 java2d.Tools$3 13: 192 61440 <objArrayKlassKlass> 14: 219 55640 [F 15: 2114 50736 java.lang.String 16: 2079 49896 java.util.HashMap$Entry 17: 528 48344 [S 18: 1940 46560 java.util.Hashtable$Entry 19: 481 46176 java.lang.Class 20: 92 43424 javax.swing.plaf.metal.MetalScrollButton ... more lines removed here to reduce output... 1118: 1 8 java.util.Hashtable$EmptyIterator 1119: 1 8 sun.java2d.pipe.SolidTextRenderer Total 61297 10152040
When the jmap -histo command is executed on a core file, the tool prints the size, count, and class name for each class. Internal classes in the HotSpot VM are prefixed with an asterisk (*).
& jmap -histo /net/koori.sfbay/onestop/jdk/6.0/promoted/all/b100/binaries/ solaris-sparcv9/bin/java core Attaching to core core from executable /net/koori.sfbay/onestop/jdk/6.0/ promoted/all/b100/binaries/solaris-sparcv9/bin/java, please wait... Debugger attached successfully. Server compiler detected. JVM version is 1.6.0-rc-b100 Iterating over heap. This may take a while... Heap traversal took 8.902 seconds. Object Histogram: Size Count Class description ------------------------------------------------------- 4151816 2941 int[] 2997816 26403 * ConstMethodKlass 2118728 26403 * MethodKlass 1613184 39750 * SymbolKlass 1268896 2011 * ConstantPoolKlass 1097040 2011 * InstanceKlassKlass 882048 1906 * ConstantPoolCacheKlass 758424 7572 char[] 733776 2518 byte[] 252240 3260 short[] 214944 2239 java.lang.Class 177448 3341 * System ObjArray 176832 7368 java.lang.String 137792 3756 java.lang.Object[] 121744 74 long[] 72960 160 java2d.Tools$3 63680 199 * ObjArrayKlassKlass 53264 158 float[] ... more lines removed here to reduce output...
The permanent generation is the area of heap that holds all the reflective data of the virtual machine itself, such as class and method objects (also called “method area” in The Java Virtual Machine Specification).
Configuring the size of the permanent generation can be
important for applications that dynamically generate and load a
very large number of classes (for example, Java Server Pages/web
containers). If an application loads “too many”
classes, then it is possible it will abort with an
OutOfMemoryError. The specific error is Exception in
thread XXXX java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space. See
![]() 3.1 Meaning of OutOfMemoryError
for a description of this and other reasons for
OutOfMemoryError.
3.1 Meaning of OutOfMemoryError
for a description of this and other reasons for
OutOfMemoryError.
To get further information about the permanent generation, you can use the -permstat option to print statistics for the objects in the permanent generation. The following example shows output from the jmap -permstat command.
$ jmap -permstat 29620 Attaching to process ID 29620, please wait... Debugger attached successfully. Client compiler detected. JVM version is 1.6.0-rc-b100 12674 intern Strings occupying 1082616 bytes. finding class loader instances ..Unknown oop at 0xd0400900 Oop's klass is 0xd0bf8408 Unknown oop at 0xd0401100 Oop's klass is null done. computing per loader stat ..done. please wait.. computing liveness.........................................done. class_loader classes bytes parent_loader alive? type <bootstrap> 1846 5321080 null live <internal> 0xd0bf3828 0 0 null live sun/misc/Launcher$ExtClassLoader@0xd8c98c78 0xd0d2f370 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0c99280 1 1440 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0b71d90 0 0 0xd0b5b9c0 live java/util/ResourceBundle$RBClassLoader@0xd8d042e8 0xd0d2f4c0 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0b5bf98 1 920 0xd0b5bf38 dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0c99248 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0d2f488 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0b5bf38 6 11832 0xd0b5b9c0 dead sun/reflect/misc/MethodUtil@0xd8e8e560 0xd0d2f338 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0d2f418 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0d2f3a8 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0b5b9c0 317 1397448 0xd0bf3828 live sun/misc/Launcher$AppClassLoader@0xd8cb83d8 0xd0d2f300 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0d2f3e0 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0ec3968 1 1440 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0e0a248 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0c99210 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0d2f450 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0d2f4f8 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 0xd0e0a280 1 904 null dead sun/reflect/DelegatingClassLoader@0xd8c22f50 total = 22 2186 6746816 N/A alive=4, dead=18 N/A
For each class loader object, the following details are printed:
The address of the class loader object at the snapshot when the utility was run
The number of classes loaded
The approximate number of bytes consumed by meta-data for all classes loaded by this class loader
The address of the parent class loader (if any)
A “live” or “dead” indication of whether the loader object will be garbage collected in the future
The class name of this class loader
The jps utility lists the instrumented HotSpot Virtual Machines for the current user on the target system. The utility is very useful in environments where the VM is embedded, that is, it is started using the JNI Invocation API rather than the java launcher. In these environments it is not always easy to recognize the Java processes in the process list.
The following example demonstrates the usage of the jps utility.
$ jps 16217 MyApplication 16342 jps
The utility lists the virtual machines for which the user has access rights. This is determined by operating-system-specific access-control mechanisms. On Solaris OS, for example, if a non-root user executes the jps utility, the output is a list of the virtual machines that were started with that user's uid.
In addition to listing the process ID, the utility provides options to output the arguments passed to the application's main method, the complete list of VM arguments, and the full package name of the application's main class. The jps utility can also list processes on a remote system if the remote system is running the jstat daemon (jstatd).
If you are running several Java Web Start applications on a system, they tend to look the same, as shown in the following example:
$ jps
1271 jps
1269 Main
1190 Main
In this case, use jps -m to distinguish them, as follows:
$ jps -m
1271 jps -m
1269 Main http://bugster.central.sun.com/bugster.jnlp
1190 Main http://webbugs.sfbay/IncidentManager/incident.jnlp
For more information on the jps utility, refer to the man page.
The utility is included in the JDK download for all operating system platforms supported by Sun.
Note - The HotSpot instrumentation is not accessible on Windows 98 or Windows ME. In addition, the instrumentation might not be accessible on Windows if the temporary directory is on a FAT32 file system.
The jrunscript utility is a command-line script shell. It supports script execution in both interactive mode and in batch mode. By default, the shell uses JavaScript, but you can specify any other scripting language for which you supply the path to the script engines's JAR file of .class files.
Thanks to the communication between the Java language and the scripting language, the jrunscript utility supports an exploratory programming style.
For more information on the jrunscript utility, refer to the man page.
The Serviceability Agent Debug Daemon (jsadebugd) attaches to a Java process or to a core file and acts as a debug server. This utility is currently available only on Solaris OS and Linux. Remote clients such as jstack, jmap, and jinfo can attach to the server using Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI).
For more information on jsadebugd, refer to the man page.
The jstack command-line utility attaches to the specified process or core file and prints the stack traces of all threads that are attached to the virtual machine, including Java threads and VM internal threads, and optionally native stack frames. The utility also performs deadlock detection.
The utility can also use the jsadebugd daemon to query a process or core file on a remote machine. Note that the output takes longer to print in this case.
A stack trace of all threads can be useful in diagnosing a number of issues such as deadlocks or hangs.
The JDK 7 release introduced the -l option, which instructs the utility to look for ownable synchronizers in the heap and print information about java.util.concurrent.locks. Without this option, the thread dump includes information only on monitors.
Starting with JDK 7, the output from the jstack
pid option is the same as that obtained by pressing
Ctrl-\ at the application console (standard input) or by sending
the process a QUIT signal. See ![]() 2.15 Ctrl-Break
Handler for an output example.
2.15 Ctrl-Break
Handler for an output example.
Thread dumps can also be obtained programmatically using the Thread.getAllStackTraces method, or in the debugger using the debugger option to print all thread stacks (the where command in the case of the jdb sample debugger).
For more information on the jstack utility , refer to the man page.
If the jstack pid command does not respond because of a hung process, the -F option can be used (on Solaris OS and Linux only) to force a stack dump, as in the following example:
$ jstack -F 8321 Attaching to process ID 8321, please wait... Debugger attached successfully. Client compiler detected. JVM version is 1.6.0-rc-b100 Deadlock Detection: Found one Java-level deadlock: ============================= "Thread2": waiting to lock Monitor@0x000af398 (Object@0xf819aa10, a java/lang/String), which is held by "Thread1" "Thread1": waiting to lock Monitor@0x000af400 (Object@0xf819aa48, a java/lang/String), which is held by "Thread2" Found a total of 1 deadlock. Thread t@2: (state = BLOCKED) Thread t@11: (state = BLOCKED) - Deadlock$DeadlockMakerThread.run() @bci=108, line=32 (Interpreted frame) Thread t@10: (state = BLOCKED) - Deadlock$DeadlockMakerThread.run() @bci=108, line=32 (Interpreted frame) Thread t@6: (state = BLOCKED) Thread t@5: (state = BLOCKED) - java.lang.Object.wait(long) @bci=-1107318896 (Interpreted frame) - java.lang.Object.wait(long) @bci=0 (Interpreted frame) - java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove(long) @bci=44, line=116 (Interpreted frame) - java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove() @bci=2, line=132 (Interpreted frame) - java.lang.ref.Finalizer$FinalizerThread.run() @bci=3, line=159 (Interpreted frame) Thread t@4: (state = BLOCKED) - java.lang.Object.wait(long) @bci=0 (Interpreted frame) - java.lang.Object.wait(long) @bci=0 (Interpreted frame) - java.lang.Object.wait() @bci=2, line=485 (Interpreted frame) - java.lang.ref.Reference$ReferenceHandler.run() @bci=46, line=116 (Interpreted frame)
To obtain stack traces from a core dump, execute the following command:
$ jstack $JAVA_HOME/bin/java core
The jstack utility can also be used to print a mixed stack, that is, it can print native stack frames in addition to the Java stack. Native frames are the C/C++ frames associated with VM code and JNI/native code.
To print a mixed stack, use the -m option, as in the following example:
$ jstack -m 21177 Attaching to process ID 21177, please wait... Debugger attached successfully. Client compiler detected. JVM version is 1.6.0-rc-b100 Deadlock Detection: Found one Java-level deadlock: ============================= "Thread1": waiting to lock Monitor@0x0005c750 (Object@0xd4405938, a java/lang/String), which is held by "Thread2" "Thread2": waiting to lock Monitor@0x0005c6e8 (Object@0xd4405900, a java/lang/String), which is held by "Thread1" Found a total of 1 deadlock. ----------------- t@1 ----------------- 0xff2c0fbc __lwp_wait + 0x4 0xff2bc9bc _thrp_join + 0x34 0xff2bcb28 thr_join + 0x10 0x00018a04 ContinueInNewThread + 0x30 0x00012480 main + 0xeb0 0x000111a0 _start + 0x108 ----------------- t@2 ----------------- 0xff2c1070 ___lwp_cond_wait + 0x4 0xfec03638 bool Monitor::wait(bool,long) + 0x420 0xfec9e2c8 bool Threads::destroy_vm() + 0xa4 0xfe93ad5c jni_DestroyJavaVM + 0x1bc 0x00013ac0 JavaMain + 0x1600 0xff2bfd9c _lwp_start ----------------- t@3 ----------------- 0xff2c1070 ___lwp_cond_wait + 0x4 0xff2ac104 _lwp_cond_timedwait + 0x1c 0xfec034f4 bool Monitor::wait(bool,long) + 0x2dc 0xfece60bc void VMThread::loop() + 0x1b8 0xfe8b66a4 void VMThread::run() + 0x98 0xfec139f4 java_start + 0x118 0xff2bfd9c _lwp_start ----------------- t@4 ----------------- 0xff2c1070 ___lwp_cond_wait + 0x4 0xfec195e8 void os::PlatformEvent::park() + 0xf0 0xfec88464 void ObjectMonitor::wait(long long,bool,Thread*) + 0x548 0xfe8cb974 void ObjectSynchronizer::wait(Handle,long long,Thread*) + 0x148 0xfe8cb508 JVM_MonitorWait + 0x29c 0xfc40e548 * java.lang.Object.wait(long) bci:0 (Interpreted frame) 0xfc40e4f4 * java.lang.Object.wait(long) bci:0 (Interpreted frame) 0xfc405a10 * java.lang.Object.wait() bci:2 line:485 (Interpreted frame) ... more lines removed here to reduce output... ----------------- t@12 ----------------- 0xff2bfe3c __lwp_park + 0x10 0xfe9925e4 AttachOperation*AttachListener::dequeue() + 0x148 0xfe99115c void attach_listener_thread_entry(JavaThread*,Thread*) + 0x1fc 0xfec99ad8 void JavaThread::thread_main_inner() + 0x48 0xfec139f4 java_start + 0x118 0xff2bfd9c _lwp_start ----------------- t@13 ----------------- 0xff2c1500 _door_return + 0xc ----------------- t@14 ----------------- 0xff2c1500 _door_return + 0xc
Frames that are prefixed with '*' are Java frames, while frames that are not prefixed with '*' are native C/C++ frames.
The output of the utility can be piped through c++filt to demangle C++ mangled symbol names. Because the HotSpot Virtual Machine is developed in the C++ language, the jstack utility prints C++ mangled symbol names for the HotSpot internal functions. The c++filt utility is delivered with the native c++ compiler suite: SUNWspro on Solaris OS and gnu on Linux.
The jstat utility uses the built-in instrumentation in the HotSpot VM to provide information on performance and resource consumption of running applications. The tool can be used when diagnosing performance issues, and in particular issues related to heap sizing and garbage collection. The jstat utility does not require the VM to be started with any special options. The built-in instrumentation in the HotSpot VM is enabled by default. The utility is included in the JDK download for all operating system platforms supported by Sun.
Note - The instrumentation is not accessible on Windows 98 or Windows ME. In addition, instrumentation is not accessible on Windows NT, 2000, or XP if a FAT32 file system is used.
The following list presents the options for the jstat utility.
class - prints statistics on the behavior of the class loader.
compiler - prints statistics of the behavior of the HotSpot compiler.
gc - prints statistics of the behavior of the garbage collected heap.
gccapacity - prints statistics of the capacities of the generations and their corresponding spaces.
gccause - prints the summary of garbage collection statistics (same as -gcutil), with the cause of the last and current (if applicable) garbage collection events.
gcnew - prints statistics of the behavior of the new generation.
gcnewcapacity - prints statistics of the sizes of the new generations and its corresponding spaces.
gcold - prints statistics of the behavior of the old and permanent generations.
gcoldcapacity - prints statistics of the sizes of the old generation.
gcpermcapacity - prints statistics of the sizes of the permanent generation.
gcutil - prints a summary of garbage collection statistics.
printcompilation - prints HotSpot compilation method statistics.
For a complete description of the jstat utility, refer to the man page.
The documentation includes a number of examples, and a few of those examples are repeated here in this document.
The jstat utility uses a vmid to identify the target process. The documentation describes the syntax of a vmid but in the simplest case a vmid can be a local virtual machine identifier. In the case of Solaris OS, Linux, and Windows, it can be considered to be the process ID. Note that this is typical but may not always be the case.
The jstat tool provides data similar to the data provided by the tools vmstat and iostat on Solaris OS and Linux.
For a graphical representation of the data, you can use the
visualgc tool. See ![]() 2.14 visualgc
Tool.
2.14 visualgc
Tool.
Below is an example of the -gcutil option. The utility attaches to lvmid 2834, takes nine samples at 250 millisecond intervals, and displays the output.
$ jstat -gcutil 2834 250 9 S0 S1 E O P YGC YGCT FGC FGCT GCT 0.00 0.00 87.14 46.56 96.82 54 1.197 140 86.559 87.757 0.00 0.00 91.90 46.56 96.82 54 1.197 140 86.559 87.757 0.00 0.00 100.00 46.56 96.82 54 1.197 140 86.559 87.757 0.00 27.12 5.01 54.60 96.82 55 1.215 140 86.559 87.774 0.00 27.12 11.22 54.60 96.82 55 1.215 140 86.559 87.774 0.00 27.12 13.57 54.60 96.82 55 1.215 140 86.559 87.774 0.00 27.12 18.05 54.60 96.82 55 1.215 140 86.559 87.774 0.00 27.12 23.85 54.60 96.82 55 1.215 140 86.559 87.774 0.00 27.12 27.32 54.60 96.82 55 1.215 140 86.559 87.774
The output of this example shows that a young generation collection occurred between the third and fourth samples. The collection took 0.017 seconds and promoted objects from the eden space (E) to the old space (O), resulting in an increase of old space utilization from 46.56% to 54.60%.
The following example illustrates the -gcnew option. The utility attaches to lvmid 2834, takes samples at 250 millisecond intervals, and displays the output. In addition, it uses the -h3 option to display the column header after every 3 lines of data.
$ jstat -gcnew -h3 2834 250 S0C S1C S0U S1U TT MTT DSS EC EU YGC YGCT 192.0 192.0 0.0 0.0 15 15 96.0 1984.0 942.0 218 1.999 192.0 192.0 0.0 0.0 15 15 96.0 1984.0 1024.8 218 1.999 192.0 192.0 0.0 0.0 15 15 96.0 1984.0 1068.1 218 1.999 S0C S1C S0U S1U TT MTT DSS EC EU YGC YGCT 192.0 192.0 0.0 0.0 15 15 96.0 1984.0 1109.0 218 1.999 192.0 192.0 0.0 103.2 1 15 96.0 1984.0 0.0 219 2.019 192.0 192.0 0.0 103.2 1 15 96.0 1984.0 71.6 219 2.019 S0C S1C S0U S1U TT MTT DSS EC EU YGC YGCT 192.0 192.0 0.0 103.2 1 15 96.0 1984.0 73.7 219 2.019 192.0 192.0 0.0 103.2 1 15 96.0 1984.0 78.0 219 2.019 192.0 192.0 0.0 103.2 1 15 96.0 1984.0 116.1 219 2.019
In addition to showing the repeating header string, this example shows that between the fourth and fifth samples, a young generation collection occurred, whose duration was 0.02 seconds. The collection found enough live data that the survivor space 0 utilization (S1U) would have exceeded the desired survivor size (DSS). As a result, objects were promoted to the old generation (not visible in this output), and the tenuring threshold (TT) was lowered from 15 to 1.
The following example illustrates the -gcoldcapacity option. The utility attaches to lvmid 21891 and takes 3 samples at 250 millisecond intervals. The -t option is used to generate a time stamp for each sample in the first column.
$ jstat -gcoldcapacity -t 21891 250 3
Timestamp OGCMN OGCMX OGC OC YGC FGC FGCT GCT
150.1 1408.0 60544.0 11696.0 11696.0 194 80 2.874 3.799
150.4 1408.0 60544.0 13820.0 13820.0 194 81 2.938 3.863
150.7 1408.0 60544.0 13820.0 13820.0 194 81 2.938 3.863
The Timestamp column reports the elapsed time in seconds since the start of the target Java VM. In addition, the -gcoldcapacity output shows the old generation capacity (OGC) and the old space capacity (OC) increasing as the heap expands to meet allocation or promotion demands. The old generation capacity (OGC) has grown from 11696 KB to 13820 KB after the 81st Full GC (FGC). The maximum capacity of the generation (and space) is 60544 KB (OGCMX), so it still has room to expand.
The jstatd daemon is a Remote Method Invocation (RMI) server application that monitors the creation and termination of instrumented Java HotSpot virtual machines and provides an interface to allow remote monitoring tools to attach to Java VMs running on the local host. For example, this daemon allows the jps utility to list processes on a remote system.
Note - The instrumentation is not accessible on Windows 98 or Windows ME. In addition, instrumentation is not accessible on Windows NT, 2000, or XP if a FAT32 file system is used.
For more information about the jstatd daemon, including detailed usage examples, refer to the man page.
The visualgc tool is related to the jstat
tool. (See ![]() 2.12 jstat
Utility.) The visualgc tool provides a graphical view
of the garbage collection (GC) system. As with jstat, it
uses the built-in instrumentation of the HotSpot VM.
2.12 jstat
Utility.) The visualgc tool provides a graphical view
of the garbage collection (GC) system. As with jstat, it
uses the built-in instrumentation of the HotSpot VM.
The visualgc tool is not included in the JDK release but is available as a separate download from the jvmstat 3.0 site.
The following screen output demonstrates how the GC and heap are visualized.
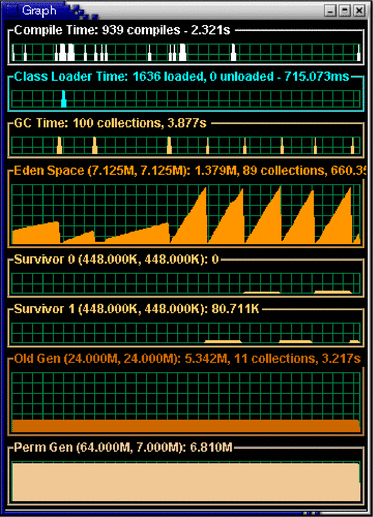
On Solaris OS or Linux, the combination of pressing the Ctrl key and the backslash (\) key at the application console (standard input) causes the HotSpot VM to print a thread dump to the application's standard output. On Windows the equivalent key sequence is the Ctrl and Break keys. The general term for these key combinations is the Ctrl-Break handler.
On Solaris OS and Linux, a thread dump is printed if the Java process receives a QUIT signal. Therefore, the kill -QUIT pid command causes the process with ID pid to print a thread dump to the standard output.
The following subsections explain in detail the output from the Ctrl-Break handler:
The thread dump consists of the thread stack, including thread state, for all Java threads in the virtual machine. The thread dump does not terminate the application: it continues after the thread information is printed.
The following example illustrates a thread dump.
Full thread dump Java HotSpot(TM) Client VM (1.6.0-rc-b100 mixed mode):
"DestroyJavaVM" prio=10 tid=0x00030400 nid=0x2 waiting on condition [0x00000000..0xfe77fbf0]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Thread2" prio=10 tid=0x000d7c00 nid=0xb waiting for monitor entry [0xf36ff000..0xf36ff8c0]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor)
at Deadlock$DeadlockMakerThread.run(Deadlock.java:32)
- waiting to lock <0xf819a938> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0xf819a970> (a java.lang.String)
"Thread1" prio=10 tid=0x000d6c00 nid=0xa waiting for monitor entry [0xf37ff000..0xf37ffbc0]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor)
at Deadlock$DeadlockMakerThread.run(Deadlock.java:32)
- waiting to lock <0xf819a970> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0xf819a938> (a java.lang.String)
"Low Memory Detector" daemon prio=10 tid=0x000c7800 nid=0x8 runnable [0x00000000..0x00000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"CompilerThread0" daemon prio=10 tid=0x000c5400 nid=0x7 waiting on condition [0x00000000..0x00000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Signal Dispatcher" daemon prio=10 tid=0x000c4400 nid=0x6 waiting on condition [0x00000000..0x00000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Finalizer" daemon prio=10 tid=0x000b2800 nid=0x5 in Object.wait() [0xf3f7f000..0xf3f7f9c0]
java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING (on object monitor)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Native Method)
- waiting on <0xf4000b40> (a java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove(ReferenceQueue.java:116)
- locked <0xf4000b40> (a java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove(ReferenceQueue.java:132)
at java.lang.ref.Finalizer$FinalizerThread.run(Finalizer.java:159)
"Reference Handler" daemon prio=10 tid=0x000ae000 nid=0x4 in Object.wait() [0xfe57f000..0xfe57f940]
java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING (on object monitor)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Native Method)
- waiting on <0xf4000a40> (a java.lang.ref.Reference$Lock)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Object.java:485)
at java.lang.ref.Reference$ReferenceHandler.run(Reference.java:116)
- locked <0xf4000a40> (a java.lang.ref.Reference$Lock)
"VM Thread" prio=10 tid=0x000ab000 nid=0x3 runnable
"VM Periodic Task Thread" prio=10 tid=0x000c8c00 nid=0x9 waiting on condition
The output consists of a header and a stack trace for each thread. Each thread is separated by an empty line. The Java threads (threads that are capable of executing Java language code) are printed first, and these are followed by information on VM internal threads.
The header line contains the following information about the thread:
Thread name
Indication if the thread is a daemon thread
Thread priority (prio)
Thread ID (tid), which is the address of a thread structure in memory
ID of the native thread (nid)
Thread state, which indicates what the thread was doing at the time of the thread dump
Address range, which gives an estimate of the valid stack region for the thread
The following table lists the possible thread states that can be printed.
|
The thread header is followed by the thread stack.
In addition to the thread stacks, the Ctrl-Break handler executes a deadlock detection algorithm. If any deadlocks are detected, it prints additional information after the thread dump on each deadlocked thread.
Found one Java-level deadlock:
=============================
"Thread2":
waiting to lock monitor 0x000af330 (object 0xf819a938, a java.lang.String),
which is held by "Thread1"
"Thread1":
waiting to lock monitor 0x000af398 (object 0xf819a970, a java.lang.String),
which is held by "Thread2"
Java stack information for the threads listed above:
===================================================
"Thread2":
at Deadlock$DeadlockMakerThread.run(Deadlock.java:32)
- waiting to lock <0xf819a938> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0xf819a970> (a java.lang.String)
"Thread1":
at Deadlock$DeadlockMakerThread.run(Deadlock.java:32)
- waiting to lock <0xf819a970> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0xf819a938> (a java.lang.String)
Found 1 deadlock.
If the Java VM flag -XX:+PrintConcurrentLocks is set, Ctrl-Break will also print the list of concurrent locks owned by each thread.
Starting with JDK 7, the Ctrl-Break handler also prints a heap summary. This output shows the different generations (areas of the heap), with the size, the amount used, and the address range. The address range is especially useful if you are also examining the process with tools such as pmap.
Heap
def new generation total 1152K, used 435K [0x22960000, 0x22a90000, 0x22e40000
)
eden space 1088K, 40% used [0x22960000, 0x229ccd40, 0x22a70000)
from space 64K, 0% used [0x22a70000, 0x22a70000, 0x22a80000)
to space 64K, 0% used [0x22a80000, 0x22a80000, 0x22a90000)
tenured generation total 13728K, used 6971K [0x22e40000, 0x23ba8000, 0x269600
00)
the space 13728K, 50% used [0x22e40000, 0x2350ecb0, 0x2350ee00, 0x23ba8000)
compacting perm gen total 12288K, used 1417K [0x26960000, 0x27560000, 0x2a9600
00)
the space 12288K, 11% used [0x26960000, 0x26ac24f8, 0x26ac2600, 0x27560000)
ro space 8192K, 62% used [0x2a960000, 0x2ae5ba98, 0x2ae5bc00, 0x2b160000)
rw space 12288K, 52% used [0x2b160000, 0x2b79e410, 0x2b79e600, 0x2bd60000)
If the Java VM flag -XX:+PrintClassHistogram is set, then the Ctrl-Break handler will produce a heap histogram.
This section lists a number of operating-system-specific tools that are useful for troubleshooting or monitoring purposes. A brief description is provided for each tool. For further details, refer to the operating system documentation (or man pages in the case of Solaris OS and Linux).
The following tools are provided by the Solaris Operating
System. See also ![]() 2.16.4 Tools Introduced
in Solaris 10 OS, which gives details for some of the tools
that were introduced in version 10 of Solaris OS.
2.16.4 Tools Introduced
in Solaris 10 OS, which gives details for some of the tools
that were introduced in version 10 of Solaris OS.
|
The following tools are provided by the Linux Operating System.
|
The following tools are provided by the Windows Operating System. In addition, you can access the MSDN Library site and search for debug support.
|
This section provides details for some of the diagnostic tools that were introduced in version 10 of the Solaris Operating System.
The pmap utility was improved in Solaris 10 OS to print stack segments with the text [stack]. This text helps you to locate the stack easily.
The following example shows some output from this tool.
19846: /net/myserver/export1/user/j2sdk6/bin/java -Djava.endorsed.d 00010000 72K r-x-- /export/disk09/jdk/6/rc/b63/binaries/solsparc/bin/java 00030000 16K rwx-- /export/disk09/jdk/6/rc/b63/binaries/solsparc/bin/java 00034000 32544K rwx-- [ heap ] D1378000 32K rwx-R [ stack tid=44 ] D1478000 32K rwx-R [ stack tid=43 ] D1578000 32K rwx-R [ stack tid=42 ] D1678000 32K rwx-R [ stack tid=41 ] D1778000 32K rwx-R [ stack tid=40 ] D1878000 32K rwx-R [ stack tid=39 ] D1974000 48K rwx-R [ stack tid=38 ] D1A78000 32K rwx-R [ stack tid=37 ] D1B78000 32K rwx-R [ stack tid=36 ] [.. more lines removed here to reduce output ..] FF370000 8K r-x-- /usr/lib/libsched.so.1 FF380000 8K r-x-- /platform/sun4u-us3/lib/libc_psr.so.1 FF390000 16K r-x-- /lib/libthread.so.1 FF3A4000 8K rwx-- /lib/libthread.so.1 FF3B0000 8K r-x-- /lib/libdl.so.1 FF3C0000 168K r-x-- /lib/ld.so.1 FF3F8000 8K rwx-- /lib/ld.so.1 FF3FA000 8K rwx-- /lib/ld.so.1 FFB80000 24K ----- [ anon ] FFBF0000 64K rwx-- [ stack ] total 167224K
Prior to the Solaris 10 OS release, the pstack utility did not support the Java language. It printed hexadecimal addresses for both interpreted and (HotSpot) compiled Java methods.
Starting in Solaris 10 OS, the pstack command-line tool prints mixed mode stack traces (Java and C/C++ frames) from a core file or a live process. The tool prints Java method names for interpreted, compiled and inlined Java methods.
Solaris 10 OS includes the DTrace tool, which allows dynamic tracing of the operating system kernel and user-level programs. This tool supports scripting at system-call entry and exit, at user-mode function entry and exit, and at many other probe points. The scripts are written in the D programming language, which is a C-like language with safe pointer semantics. These scripts can help you in troubleshooting problems or solving performance issues.
The dtrace command is a generic front-end to the DTrace tool. This command provides a simple interface to invoke the D language, to retrieve buffered trace data, and to access a set of basic routines to format and print traced data.
You may write your own customized DTrace scripts, using the D language, or download and use one or more of the many scripts that are already available on various sites.
The probes are delivered and instrumented by kernel modules called providers. The types of tracing offered by the probe providers include user instruction tracing, function boundary tracing, kernel lock instrumentation, profile interrupt, system call tracing, and much more. If you write your own scripts, you use the D language to enable the probes; this language also allows conditional tracing and output formatting.
You can use the dtrace -l option to explore the set of providers and probes that are available on your Solaris OS.
The DTrace Toolkit is a collection of useful documented scripts developed by the OpenSolaris DTrace community. See http://www.opensolaris.org/os/community/dtrace/dtracetoolkit/
Details on DTrace are provided at the following locations:
Solaris Dynamic Tracing Guide: http://docs.sun.com/app/docs/doc/817-6223/
BigAdmin System Administration Portal for DTrace: http://www.sun.com/bigadmin/content/dtrace/
Starting with JDK 7, the Java HotSpot VM contains two built-in probe providers: hotspot and hotspot_jni. These providers deliver probes that can be used to monitor the internal state and activities of the VM, as well as the Java application that is running.
The hotspot provider probes can be categorized as follows:
VM lifecycle: VM initialization begin and end, and VM shutdown.
Thread lifecycle: thread start and stop, thread name, thread ID, and so on.
Class-loading: Java class loading and unloading.
Garbage collection: start and stop of garbage collection, system-wide or by memory pool.
Method compilation: method compilation begin and end, and method loading and unloading.
Monitor probes: wait events, notification events, contended monitor entry and exit.
Application tracking: method entry and return, allocation of a Java object.
In order to call from native code to Java code, the native code must make a call through the JNI interface. The hotspot_jni provider manages DTrace probes at the entry point and return point for each of the methods that the JNI interface provides for invoking Java code and examining the state of the VM.
At probe points, you can print the stack trace current thread using the ustack built-in function. This function prints Java method names in addition to C/C++ native function names. The following is a simple D script that prints a full stack trace whenever a thread calls the read system call.
#!/usr/sbin/dtrace -s
syscall::read:entry
/pid == $1 && tid == 1/ {
ustack(50, 0x2000);
}
The above script is stored in a file named read.d and is run with the following command:
read.d pid-of-the-Java-process-that-is-traced
If your Java application generated a lot of I/O or had some unexpected latency, the use of the DTrace tool and its ustack() action can help you diagnose the problem.
The JDK software has extensive Application Programing Interfaces (APIs) which can be used to develop tools to observe, monitor, profile, debug, and diagnose issues in applications that are deployed on the Java runtime environment. The development of new tools is beyond the scope of this document. Instead this section provides a brief overview of the programming interfaces available. Refer also to example and demonstration code that is included in the JDK download.
The java.lang.management package provides the management interface for monitoring and management of the Java Virtual Machine and the operating system. Specifically it covers interfaces for the following systems:
Class loading
Compilation
Garbage collection
Memory manager
Runtime
Threads
The java.lang.management package is fully described in the Java SE API documentation.
The JDK release includes example code that demonstrates the usage of the java.lang.management package. These examples can be found in the $JAVA_HOME/demo/management directory. Some of these examples are as follows:
MemoryMonitor - demonstrates the use of the java.lang.management API to observe the memory usage of all memory pools consumed by the application.
FullThreadDump - demonstrates the use of the java.lang.management API to get a full thread dump and detect deadlocks programmatically.
VerboseGC - demonstrates the use of the java.lang.management API to print the garbage collection statistics and memory usage of an application.
In addition to the java.lang.management package, the JDK release includes platform extensions in the com.sun.management package. The platform extensions include a management interface to obtain detailed statistics from garbage collectors that perform collections in cycles. These extensions also include a management interface to obtain additional memory statistics from the operating system.
Details on the platform extensions can be found at Java SE API documentation: Monitoring and Management Interface for the Java Platform.
The java.lang.instrument package provides services that allow Java programming language agents to instrument programs running on the Java VM. Instrumentation is used by tools such as profilers, tools for tracing method calls, and many others. The package facilitates both load-time and dynamic instrumentation. It also includes methods to obtain information on the loaded classes and information about the amount of storage consumed by a given object.
The java.lang.instrument package is fully described in the Java SE API documentation.
The java.lang.Thread class has a static method called getAllStackTraces, which returns a map of stack traces for all live threads. The Thread class also has a method called getState, which returns the thread state; states are defined by the java.lang.Thread.State enumeration. These methods can be useful when adding diagnostic or monitoring capabilities to an application. These methods are fully described in the API documentation.
The Java Virtual Machine Tools Interface (JVM TI) is a native (C/C++) programming interface that can be used to develop a wide range of developing and monitoring tools. JVM TI provides an interface for the full breadth of tools that need access to VM state, including but not limited to profiling, debugging, monitoring, thread analysis, and coverage analysis tools.
Some examples of agents that rely on JVM TI are the following:
HPROF profiler (see ![]() 2.1 HPROF - Heap
Profiler)
2.1 HPROF - Heap
Profiler)
Java Debug Wire Protocol (JDWP) agent (see ![]() 2.17.5 Java Platform
Debugger Architecture)
2.17.5 Java Platform
Debugger Architecture)
java.lang.instrument implementation (see ![]() 2.17.2
java.lang.instrument Package)
2.17.2
java.lang.instrument Package)
The specification for JVM TI can be found in the JVM Tool Interface documentation.
The JDK release includes example code that demonstrates the usage of JVM TI. These examples can be found in the $JAVA_HOME/demo/jvmti directory. Some of the examples are as follows:
mtrace - an agent library that tracks method call and return counts. It uses byte-code instrumentation to instrument all classes loaded into the virtual machine and prints a sorted list of the frequently used methods.
heapTracker - an agent library that tracks object allocation. It uses byte-code instrumentation to instrument constructor methods.
heapViewer - an agent library that prints heap statistics when Ctrl-\ or Ctrl-Break is pressed. For each loaded class it prints an instance count of that class and the space used.
The Java Platform Debugger Architecture (JPDA) is the architecture designed for use by debuggers and debugger-like tools. It consists of two programming interfaces and a wire protocol.
The Java Virtual Machine Tools Interface (JVM TI) is the
interface to the virtual machine (as described in ![]() 2.17.4
Java Virtual Machine Tools Interface).
2.17.4
Java Virtual Machine Tools Interface).
The Java Debug Interface (JDI) defines information and requests at the user code level. It is a pure Java programming language interface for debugging Java programming language applications. In JPDA, the JDI is a remote view in the debugger process of a virtual machine in the debuggee process. It is implemented by the front-end, while a debugger-like application (for example, IDE, debugger, tracer, monitoring tool, and so forth) is the client.
The Java Debug Wire Protocol (JDWP) defines the format of information and requests transferred between the process being debugged and the debugger front end, which implements the JDI.
A complete description (including specifications) for JPDA is located in the Java Platform Debugger Architecture (JPDA) documentation.
A graphic view of the JPDA structure is presented in the Java Platform Debugger Architecture description.
The jdb utility is included in the JDK release as the
example command-line debugger. The jdb utility uses the
Java Debug Interface (JDI) to launch or connect to the target VM.
See ![]() 2.4 jdb Utility.
2.4 jdb Utility.
In addition to traditional debugger-type tools, JDI can also be
used to develop tools that help in post-mortem diagnostics and
scenarios where the tool needs to attach to a process in a
non-cooperative manner (a hung process, for example). See
![]() 2.4 jdb Utility for a description of the JDI
connectors which can be used to attach a JDI-based tool to a crash
dump or hung process.
2.4 jdb Utility for a description of the JDI
connectors which can be used to attach a JDI-based tool to a crash
dump or hung process.